Chapters:
- Chapter 3: “Lists” (pp.62-73)
- Chapter 13: “Boxes” (pp.300-329)
- Chapter2: “Basic JavaScript Instructions”
- chapter 4: “Decisions and Loops” from switch statements
Chapter 3: “Lists”
- Numbered list
- WHAT : They are the ordered list.
- WHY : it is used if the lists must be ordere for example if they are steps.
- HOW : There is a tag for it
<ol></ol>- Each list placed in
<li></li>tag.
- Each list placed in

- Bullet list
- WHAT : They are the unordered list.
- WHY : it is used if the lists not important be ordere for example if they are types of s.th.
- HOW : There is a tag for it
<ul></ul>- Each list placed in
<li></li>tag.
- Each list placed in
- Definision list
- WHAT : They are list of defntions.
- WHY : it is used if the lists have a lot of definsions
- HOW : There is a tag for it
<dl></dl>- Each list placed in
<dt></dt>tag. for the term - Each list placed in
<dd></dd>tag. for the definsion
- Each list placed in
2. Chapter 13: “Boxes”
- controlling size of boxing
- width and height
- by defualt the box will be big to cintain the contenet.
- you can use many measurements (pix,percentage,ems)
- min width-max width
- its a properity to ensure that the content fits any user’s screen
- min- width to ensure that its is not too narrow in big screens while the max stands for the oppisite.
- max height- min height
- same as min width but the difference is stands for the height
- if the box is too heigh there will be a messey to overcome this we can use overflow
- overflow
- its a properity to adjust the contenet if its too big
- you can use hidden
- you can use scroll
- width and height
-
box model
- The CSS Box Model is a term used for the container that wraps the following element properties within it.
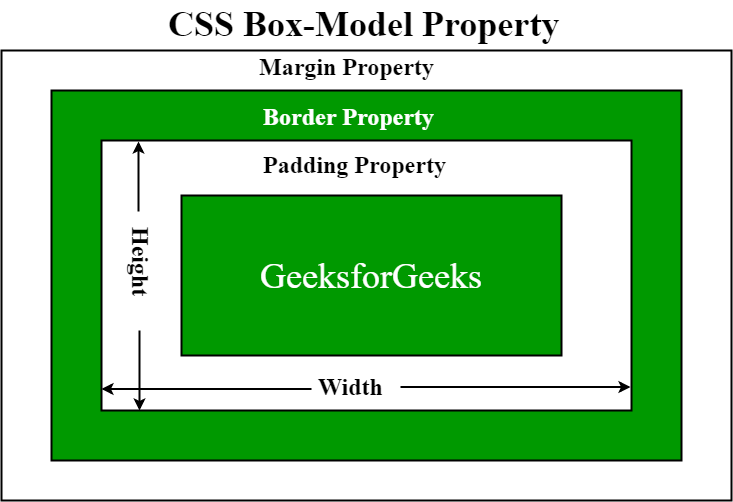
- Margin
- On the CSS Box Model, the margin is the section in the exterior. This edge extends around the box model taking the empty space between the margin and border properties. You can consider this a buffer area that separates the interior of the CSS box model from other HTML elements on a page. Note that the margin is defined by both the width and height of the box, as well as set margin properties. This can also be affected by the “box-sizing” property.
- Border
- Next, you have the Border property of the CSS Box Model. Keeping in the theme of separation, this area exists as a boundary between the margin and padding properties of the box. This area can be manipulated using the CSS Border property for styling and sizing needs.
- Padding
- The padding section of the CSS Box Model sits in the space between the HTML content and the border. As with much of the other items in the box mode, the padding can be altered through its related properties. For example, the padding can be changed through the directions of the top, right, bottom, and left sections.
For example, we can take this sample CSS code below;
div {
border-style: solid;
border-color: blue;
}
This div does not have padding defined, as such, you have the output shown in the image below.
- displaying and hiding boxes
Chapter2: “Basic JavaScript Instructions and loops”
here are situations when we want to run the code at different conditions, such as, if one condition applies run a particular code, if another condition applies another code is run. This is prioritized with “if” and “else if” conditionals as follows:
`function getColor(phrase){
if (phrase === "stop"){
console.log("red");
} else if (phrase === "slow"){
console.log("yellow");
} else if (phrase === "go"){
console.log("green");
} else {
console.log("purple");
}
}` * The switch statement is used to perform different actions based on different conditions. Syntax:
` switch(expression) {
case x:
// code block
break;
case y:
// code block
break;
default:
// code block
}`
This is how it works:
- The switch expression is evaluated once.
- The value of the expression is compared with the values of each case.
- If there is a match, the associated block of code is executed.
- If there is no match, the default code block is executed.
