Chapters
chapter 5 Forms
- The
<form>HTML element represents a document section containing interactive controls for submitting information.
It is possible to use the :valid and :invalid CSS pseudo-classes to style a <form> element based on whether or not the elements inside the form are valid.
- Attributes This element includes the global attributes.
-
accept
Comma-separated content types the server accepts. Note This attribute was removed in HTML5 and should not be used. Instead, use the accept attribute on elements. -
accept-charset
Space-separated character encodings the server accepts. The browser uses them in the order in which they are listed. The default value means the same encoding as the page. (In previous versions of HTML, character encodings could also be delimited by commas.) - autocapitalize
A nonstandard attribute used by iOS Safari that controls how textual form elements should be automatically capitalized. autocapitalize attributes on a form elements override it on <form>. Possible values:- none: No automatic capitalization.
- sentences (default): Capitalize the first letter of each sentence.
- words: Capitalize the first letter of each word.
- characters: Capitalize all characters — that is, uppercase.
- autocomplete
Indicates whether input elements can by default have their values automatically completed by the browser. autocomplete attributes on form elements override it on <form>. Possible values:- off: The browser may not automatically complete entries. (Browsers tend to ignore this for suspected login forms; see The autocomplete attribute and login fields.)
- on: The browser may automatically complete entries.
-
name
The name of the form. The value must not be the empty string, and must be unique among the form elements in the forms collection that it is in, if any. - rel
Creates a hyperlink or annotation depending on the value, see the rel attribute for details.
Attributes for form submission
The following attributes control behavior during form submission:
- action The URL that processes the form submission. This value can be overridden by a formaction attribute on a
-
enctype If the value of the method attribute is post, enctype is the MIME type of the form submission. Possible values: application/x-www-form-urlencoded: The default value. multipart/form-data: Use this if the form contains
<input>elements with type=file. text/plain: Introduced by HTML5 for debugging purposes. This value can be overridden by formenctype attributes on<button>,<input type="submit">, or<input type="image">elements. - method The HTTP method to submit the form with. Possible (case insensitive) values: post: The POST method; form data sent as the request body. get: The GET method; form data appended to the action URL with a ? separator. Use this method when the form has no side-effects. dialog: When the form is inside a

Chapter 15 Lists, Tables & Forms
- Specifying bullet point styles
- Adding borders and backgrounds to tables
- Changing the appearance of form elements
- There are several CSS properties that were created to work with
- specific types of HTML elements, such as lists, tables, and forms. Together, these properties allow you to take finer control over specific parts of your pages.
BULLET POINT STYLES
- list-style-type The list-style-type property allows you to control the shape or style of a bullet point (also known as a marker).
It can be used on rules that apply to the <ol>, <ul>, and <li> elements.



-
UNORDERED LISTS For an unordered list you can use the following values:
- none
- disc
- imagecircle
- imagesquare
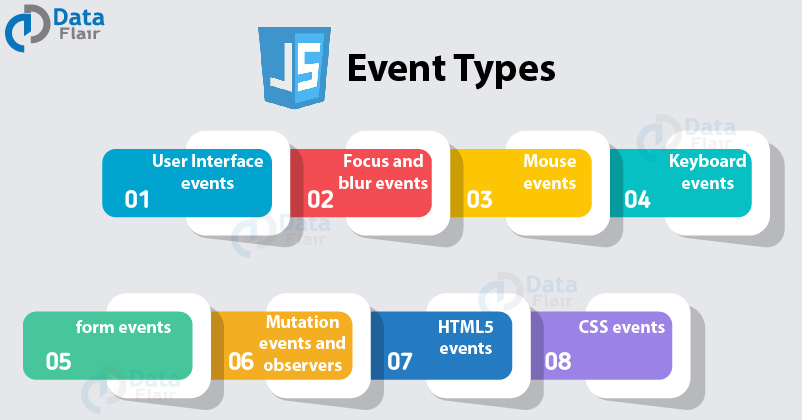
Chapter 6 Events
Events are fired to notify code of “interesting changes” that may affect code execution. These can arise from user interactions such as using a mouse or resizing a window, changes in the state of the underlying environment (e.g. low battery or media events from the operating system), and other causes.
Each event is represented by an object that is based on the Event interface, and may have additional custom fields and/or functions to provide information about what happened. The documentation for every event has a table (near the top) that includes a link to the associated event interface, and other relevant information. A full list of the different event types is given in Event > Interfaces based on Event.
This topic provides an index to the main sorts of events you might be interested in (animation, clipboard, workers etc.) along with the main classes that implement those sorts of events. At the end is a flat list of all documented events.
- Event listing
- AbortSignal
- abort event
- AudioScheduledSourceNode
- ended event
- AudioTrackList
- addtrack event
- change event
- removetrack event
- BroadcastChannel
- messageerror event
- message event
- DedicatedWorkerGlobalScope
- messageerror event
- message event