Assorted Topics
Chapter 16: “Images”
- controlling size of “Images
- aliging “Images”
- adding backgroung images.
- Controlling size of “Images:
Sometimes, it is required to fit an image into a certain given dimension. We can resize the image by specifying the width and height of an image. A common solution is to use the max-width: 100%; and height: auto; so that large images do not exceed the width of their container. The max-width and max-height properties of CSS works better, but they are not supported in many browsers.
Another way of resizing the image is by using the object-fit property, which fits the image. This CSS property specifies how a video or an image is resized to fit its content box. It defines how an element fits into the container with an established width and height.
The object-fit property is generally applied to image or video. This property defines how an element responds to the width and height of its container. Mainly there are five values of object-fit property such as fill, contain, cover, none, scale-down, initial, and inherit. The default value of this property is “fill”.
- aliging “Images”
Images are an important part of any web application. Including a lot of images in a web application is generally not recommended, but it is important to use the images wherever they required. CSS helps us to control the display of images in web applications.
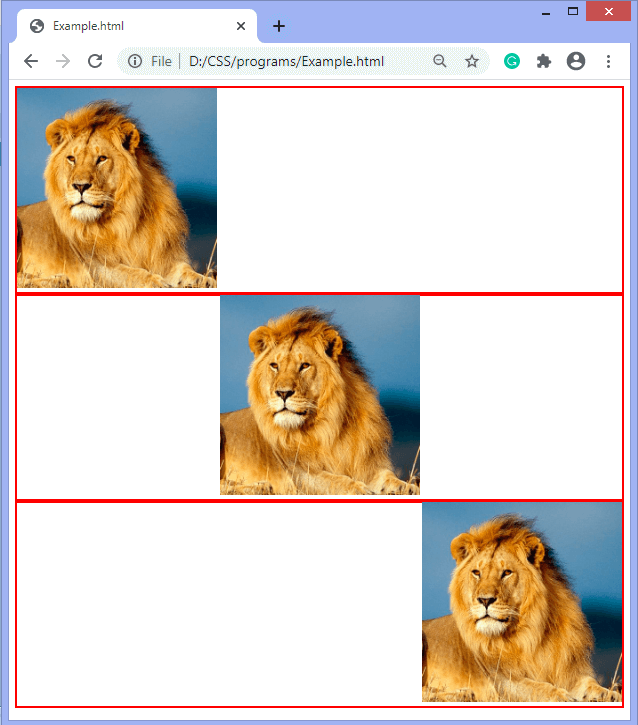
Aligning an image means to position the image at center, left and right. We can use the float property and text-align property for the alignment of images.
If the image is in the div element, then we can use the text-align property for aligning the image in the div.
-
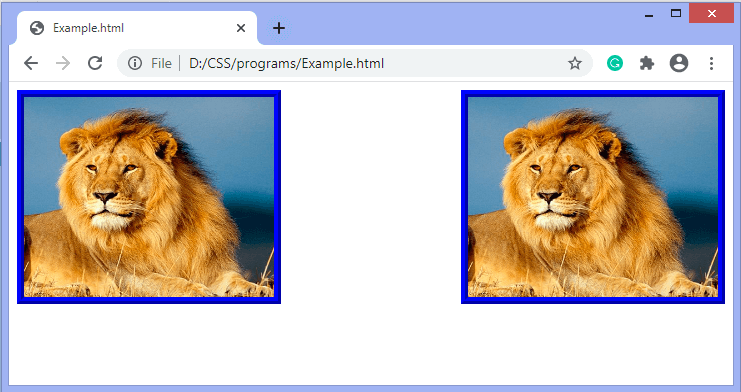
- Using float property The CSS float property is a positioning property. It is used to push an element to the left or right, allowing other elements to wrap around it. It is generally used with images and layouts.
Elements are floated only horizontally. So it is possible only to float elements left or right, not up or down. A floated element may be moved as far to the left or the right as possible. Simply, it means that a floated element can display at the extreme left or extreme right. Example In this example, we are aligning the images by using the text-align property. The images are in the div element.
-
- adding backgroung images.
The background-image CSS property sets one or more background images on an element.
The background images are drawn on stacking context layers on top of each other. The first layer specified is drawn as if it is closest to the user.
- adding backgroung images.
The borders of the element are then drawn on top of them, and the background-color is drawn beneath them. How the images are drawn relative to the box and its borders is defined by the background-clip and background-origin CSS properties
If a specified image cannot be drawn (for example, when the file denoted by the specified URI cannot be loaded), browsers handle it as they would a none value.
-
Note: Even if the images are opaque and the color won’t be displayed in normal circumstances, web developers should always specify a background-color. If the images cannot be loaded—for instance, when the network is down—the background color will be used as a fallback.
-
Syntax Each background image is specified either as the keyword none or as an
<image>value.
To specify multiple background images, supply multiple values, separated by a comma:
background-image:
linear-gradient(to bottom, rgba(255,255,0,0.5)
rgba(0,0,255,0.5))
url('catfront.png');
Chapter 19: “Practical Information”
- Search engine optimization
- Using analytics to understand visitors
- Putting your site on the web
There are entire books written about each of the topics covered in this chapter but I will introduce you to the key themes that each subject deals with and give you pointers for what you need to be considering. You will see:
- The basics of search engine optimization
- Using analytics to understand how people are using your site after it has launched
- Putting your site on the web
** SEARCH ENGINE OPTIMIZATION (SEO)**
SEO is a huge topic and several books have been written on the subject. The following pages will help you understand the key concepts so you can improve your website’s visibility on search engines.
** THE BASICS**
Search engine optimization (or SEO) is the practice of trying to help your site appear nearer the top of search engine results when people look for the topics that your website covers.
At the heart of SEO is the idea of working out which terms people are likely to enter into a search engine to find your site and then using these terms in the right places on your site to increase the chances that search engines will show a link to your site in their results.
Adding vedios and audio:
HTML5 features include native audio and video support without the need for Flash.
The HTML5
Embedding Video Here is the simplest form of embedding a video file in your webpage −
<video src = "foo.mp4" width = "300" height = "200" controls>
Your browser does not support the
</video>
The current HTML5 draft specification does not specify which video formats browsers should support in the video tag. But most commonly used video formats are −
-
- Ogg − Ogg files with Thedora video codec and Vorbis audio codec.
-
- mpeg4 − MPEG4 files with H.264 video codec and AAC audio codec.
You can use <source> tag to specify media along with media type and many other attributes. A video element allows multiple source elements and browser will use the first recognized format −
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <body> <video width = "300" height = "200" controls autoplay> <source src = "/html5/foo.ogg" type ="video/ogg" /> <source src = "/html5/foo.mp4" type = "video/mp4" /> Your browser does not support the <video> element. </video> </body> </html>
Embedding Audio HTML5 supports
<audio src = "foo.wav" controls autoplay> Your browser does not support the <audio> element. </audio>
The current HTML5 draft specification does not specify which audio formats browsers should support in the audio tag. But most commonly used audio formats are ogg, mp3 and wav.
You can use <source&ggt; tag to specify media along with media type and many other attributes. An audio element allows multiple source elements and browser will use the first recognized format −
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <body> <audio controls autoplay> <source src = "/html5/audio.ogg" type = "audio/ogg" /> <source src = "/html5/audio.wav" type = "audio/wav" /> Your browser does not support the <audio> element. </audio> </body> </html>
