Read: Linked Lists
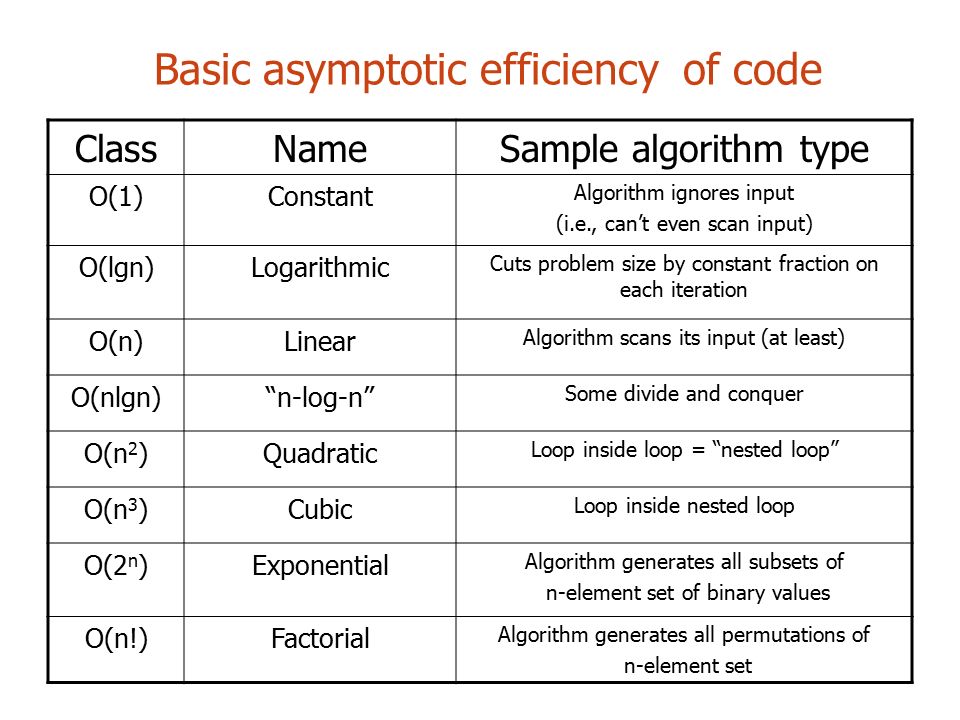
Big O: Analysis of Algorithm Efficiency :
- Big O: The worst case analysis of algorithm efficiency.
- Running Time: The amount of time required for an algorithm to complete.
- Memory Space: The amount of memory resources required for an algorithm to complete.
- Input Size: Represented by the variable n, the total size of values used as parameters in an algorithm.
- Big Omega: The best case analysis of algorithm efficiency.
- Big Theta: The typical or random case used for analysis of algorithm efficiency.
Linked Lists
- LINKED LIST
- A Linked List is a sequence of Nodes that are connected/linked to each other. The most defining feature of a Linked List is that each Node references the next Node in the link.
Node
- Nodes are the individual items/links that live in a linked list. Each node contains the data for each link.
NEXT
- Each node contains a property called Next. This property contains the reference to the next node.
HEAD-NODE
- The first node in the linked-list
TAIL-NODE
- the last node with value of properity is null
- VISULAIZE THE CONCEPT OF LINKED LIST

What’s a Linked List, Anyway pt1
- its one of the comlicated data structure we use it to organize our data
- Its main feature that it holds the linear data structure which means that there is a sequence and an order to how they are constructed and traversed
- Linked lists don’t need to take up a single block of memory; instead, the memory that they use can be scattered throughout.
-The starting point of the list is a reference to the first node, which is referred to as the head.
What’s a Linked List, Anyway pt2
- we can add elements and remove elements from a linked list.
- Linked list is made up a single node, and a node always contains some data and, most importantly, a pointer to the next node or null.
- In order ti change or reordiring we just need to figure out which pointer needs to point to where.
HOW
- First, we find the head node of the linked list.
- Next, we’ll make our new node, and set its pointer to the current first node of the list.
- Lastly, we rearrange our head node’s pointer to point at our new node.

