Readings: Socket.io
Review, Research, and Discussion
- What is the benefit of transforming data into packets?
- to meet the demands of pervasive data-centric applications and services. Packet-based networks not only enable new innovations, services, and business opportunities, they are also the most cost-effective, efficient, and scalable networks for content delivery
- UDP is often refereed to as a connectionless protocol. Why is this?
- UDP is a connectionless protocol. No connection needs to be established between the source and destination before you transmit data. UDP does not have a mechanism to make sure that the payload is not corrupted. As a result, the application must take care of data integrity all by itself.
- Can a socket server application have multiple socket connections?
- yes, it can take more than one.
- Can a socket connection application be connected to multiple socket servers?
- A connected socket is assigned to a new (dedicated) port, so it means that the number of concurrent connections is limited by the number of ports, unless multiple sockets can share the same port
- Can an application be both a socket server and a socket connection?
- yes,If you want to have a “peer-to-peer” type system, then you just have each client run both a client and a server socket - the server socket for accepting connections from other clients and the client socket for establishing connections to others.
DOCUMENTATION:
- Observer Pattern
- he Observer pattern offers a subscription model in which objects subscribe to an event and get notified when the event occurs. This pattern is the cornerstone of event driven programming, including JavaScript. The Observer pattern facilitates good object-oriented design and promotes loose coupling
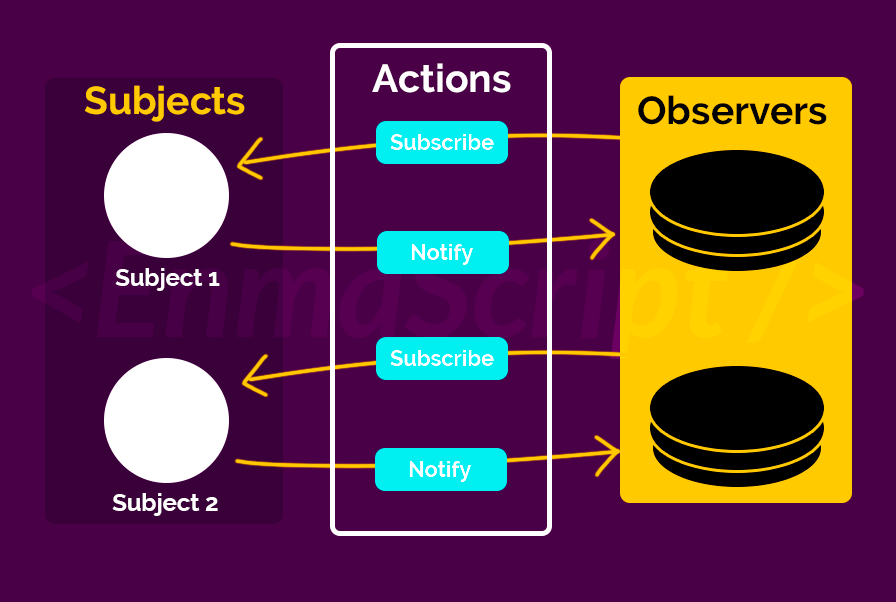
- Listener
- An event listener is a procedure in JavaScript that waits for an event to occur. The simple example of an event is a user clicking the mouse or pressing a key on the keyboard.
- Event Handler
- Event handlers are the JavaScript code that invokes a specific piece of code when a particular action happens on an HTML element. The event handler can either invoke the direct JavaScript code or a function
- Event Driven Programming
- JavaScript in the browser uses an event-driven programming model. Everything starts by following an event. The event could be the DOM is loaded, or an asynchronous request that finishes fetching, or a user clicking an element or scrolling the page, or the user types on the keyboard
- Event Loop
- The event loop is the secret behind JavaScript’s asynchronous programming

- Event Queue
- event queue is responsible for sending new functions to the track for processing. It follows the queue data structure to maintain the correct sequence in which all operations should be sent for execution.
- Call Stack
- A call stack is a mechanism for an interpreter (like the JavaScript interpreter in a web browser) to keep track of its place in a script that calls multiple functions
- Emit/Raise/Trigger
- The emit method (the publish method), on the other hand, allows you to “emit” an event, which causes all callbacks registered to the event to ‘fire’, (get called).
- database
- A database is an organized collection of structured information, or data, typically stored electronically in a computer system. A database is usually controlled by a database management system (DBMS). … The data can then be easily accessed, managed, modified, updated, controlled, and organized.
Preview
- WebSocket => is a computer communications protocol, providing full-duplex communication channels over a single TCP connection. The WebSocket protocol was standardized by the IETF as RFC 6455 in 2011, and the WebSocket API in Web IDL is being standardized by the W3C.
WebSocket is distinct from HTTP. Both protocols are located at layer 7 in the OSI model and depend on TCP at layer 4. Although they are different, RFC 6455 states that WebSocket “is designed to work over HTTP ports 443 and 80 as well as to support HTTP proxies and intermediaries,” thus making it compatible with HTTP. To achieve compatibility, the WebSocket handshake uses the HTTP Upgrade header[1] to change from the HTTP protocol to the WebSocket protocol.
Difference Between WebSocket and Socket.io
-
WebSocket => is the communication Protocol that provides bidirectional communication between the Client and the Server over a TCP connection; WebSocket remains open all the time, so they allow real-time data transfer. When clients trigger the request to the server, it does not close the connection on receiving the response; it rather persists and waits for the Client or server to terminate the request.
-
Socket.IO => is a library that enables real-time and full-duplex communication between the Client and the Web servers. It uses the WebSocket protocol to provide the interface. Generally, it is divided into two parts; both WebSocket vs Socket.io are event-driven libraries.